What You Need To Know
Researchers from Embedi discovered (and responsibly disclosed) a stack-based buffer overflow weakness in Cisco Smart Install Client code which causes the devices to be susceptible to arbitrary remote code execution without authentication.
Cisco Smart Install (SMI) is a “plug-and-play” configuration and image-management feature that provides zero-touch deployment for new (typically access layer) switches. The feature allows a customer to ship a Cisco switch to any location, install it in the network, and power it on without additional configuration requirements. The Smart Install feature incorporates no authentication by design.
Have We Been Here Before?
Yep. Rapid7’s own Jon Hart reported on Cisco Smart Install Exposure back in September of 2017. Jon’s blog post has a wealth of information on Cisco SMI exposure over the years and we’ll refrain from duplicating the historical content here.
What’s New?
Unlike previous SMI exposure reports, Cisco has officially stated this is a bona fide vulnerability and not “protocol misuse”. The issue lies in the lack of proper validation of packet data which makes it possible for attackers to send out a well-crafted sequence of packets/bytes to cause a buffer overflow which could result in:
- a device reboot
- arbitrary code execution
- application-level DoS
What’s Impacted?
This vulnerability affects Cisco devices that are running a vulnerable release of Cisco IOS or IOS XE Software and have the Smart Install client feature enabled.
Only Smart Install client switches are affected by the vulnerability that is described in this advisory. Cisco devices that are configured as a Smart Install director are not affected by this vulnerability.
To identify whether SMI is enabled on a given device, all you need to do is connect to it and issue this command:
# show vstack config
If it returns with a Role: Client (SmartInstall enabled) response or a response that includes Oper Mode: Enabled and Role: Client, the device is vulnerable.
What Can I Do?
Identify vulnerable systems in your environment and patch them as soon as possible. If you have any SMI endpoints in directly connected to the internet, you should disable SMI as soon as possible and leave it disabled.
Metasploit users can identify Smart Install endpoints with the auxiliary/scanner/misc/cisco_smart_install module.
InsightVM/Nexpose current coverage is as follows:
- Today’s (March 29, 2018) content update will contain authenticated vulnerability checks for CVE-2018-0151 and CVE-2018-0171 on the IOS platform. Authenticated vulnerability coverage for IOS XE is not yet supported. These vulnerabilities have been tagged as Rapid7 Critical.
- InsightVM customers already have visibility into exposed Smart Install instances (CVE-2018-0171) on both IOS and IOS XE. Use the vulnerability ID cisco-sr-20170214-smi in filters or searches.
- A vulnerability check for CVE-2018-0150 (static credentials in IOS XE) will be forthcoming once we have confirmed the credentials for the undocumented user account in question.
Wait…Organizations Connect Unauthenticated Administrative Ports to the Internet?
They sure do.
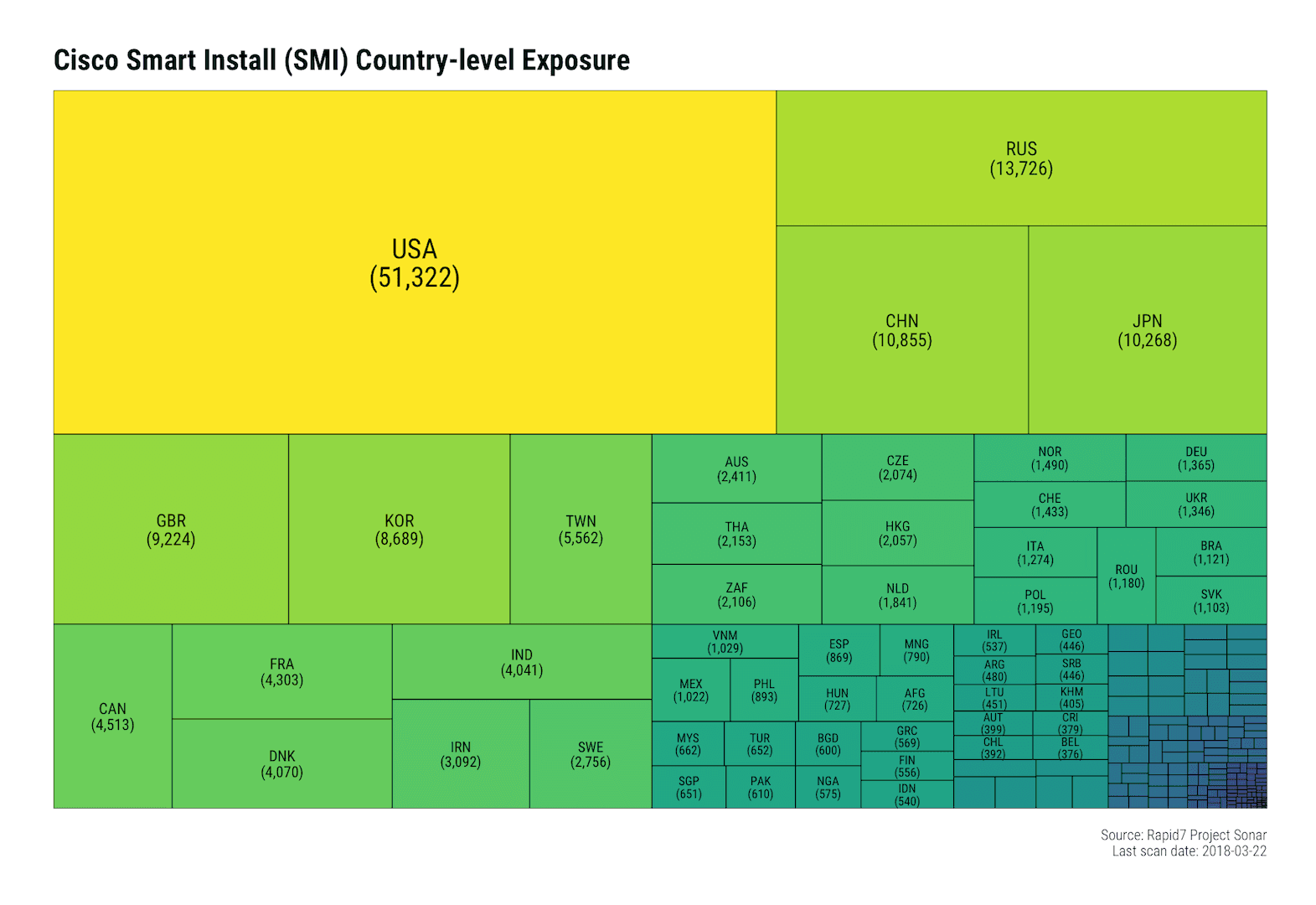
The aforementioned post by Jon Hart showed that there were over 215,000 endpoints exposing SMI to the internet back in September of 2017, Rapid7 Labs has been tracking this on a bi-weekly basis and — while the SMI exposure has steadily been reducing — there are still over 150,000 devices exposing SMI.
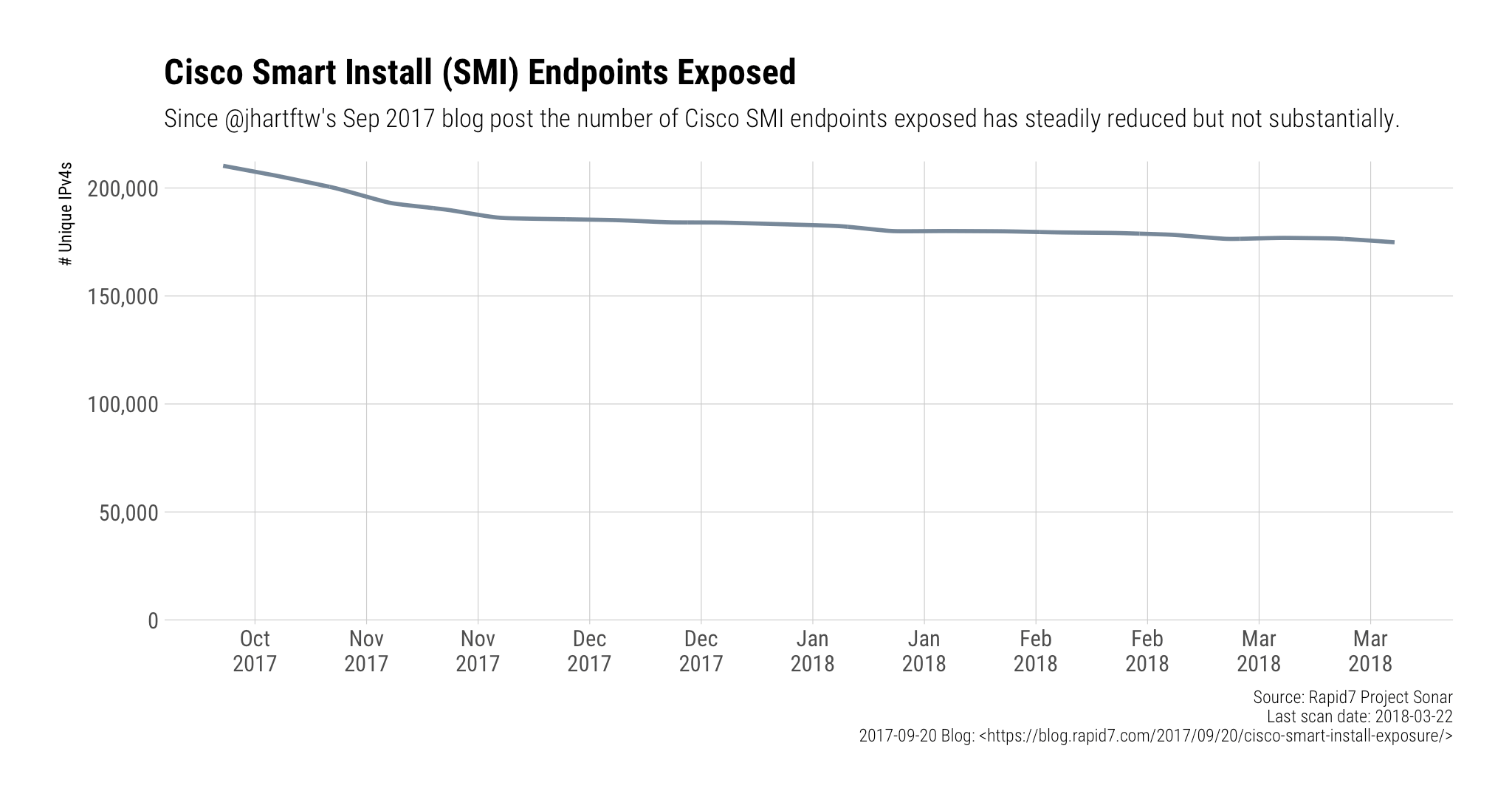
Nearly 50% of exposed devices are in the United States, Russia, China, and Japan:
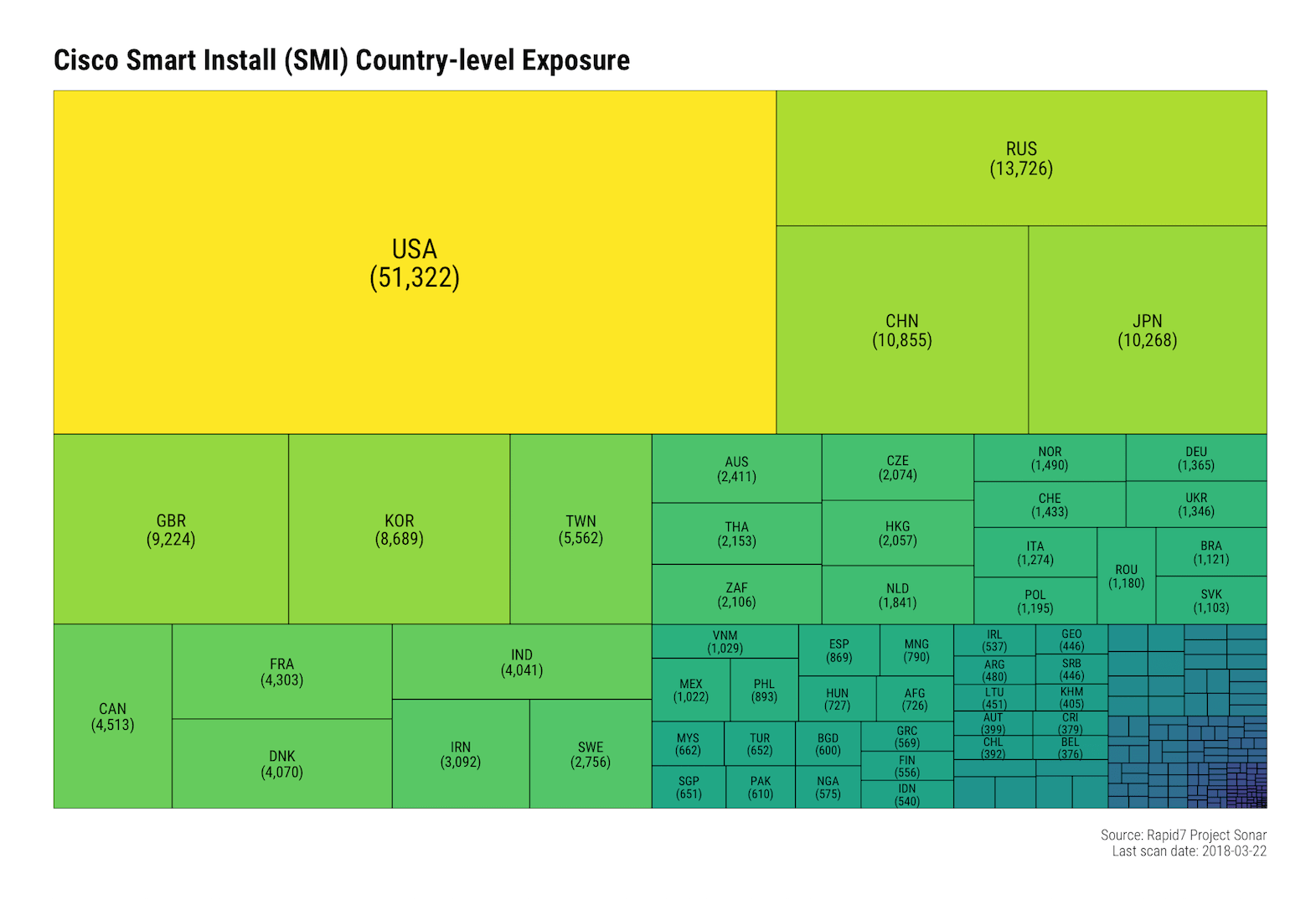
Not all of these will be vulnerable to this new weakness, but they’re all just sitting out on the wild, wild internet waiting for anyone to issue SMI instructions to them or use historical vulnerability exploits against them.
Even if you’re not impacted by the this remote code execution vulnerability, take this opportunity to heed the advice of our previous post and ensure you’ve reviewed Cisco’s SMI hardening guidelines:
- CSCvd36820 automatically disables SMI if not used during bootup.
- CSCvd36799 if SMI is enabled it must show in the running config.
- CSCvd36810 periodically alerts to the console if SMI is enabled.
For more tips and information on managing vulnerabilities check out more of Rapid7's vulnerability management blogs.