Following disclosure of the React2Shell vulnerability (CVE-2025-55182), a maximum-severity Remote Code Execution (RCE) in React Server Components (RSC) a.k.a. the Flight protocol, security teams are assessing exposure and validating fixes. React and ecosystem vendors have released patches; exploitation in the wild has been reported, so rapid validation matters.
What is React2Shell?
React2Shell is an unauthenticated RCE flaw caused by insecure Flight payload deserialization in server-side React/RSC implementations (including popular frameworks like Next.js). It carries a CVSS 10.0 rating and affects React versions 19.0.0, 19.1.0, 19.1.1, and 19.2.0 as well as Next.js versions 15.0.0-15.1.6 and 16.0.0-16.0.6 prior to recent patches. You can read more about it in this detailed CVE overview blog post.
In this detailed writeup, we will share how our customers can specifically test for React2Shell with Rapid7’s Application Security solution.
Testing for React2Shell with application security
With our dynamic application security testing (DAST) solution, customers can assess the risk of their applications. Rapid7 allows you to configure various attacks of your applications to identify response behaviors that make your applications more vulnerable to attacks. These attacks are run during scans that you can customize based on your needs. In this case, we’ve extended our RCE attack module to include a check for React2Shell.
What does this mean? Customers can now run an Attack Injection using the RCE, which includes an attack type for React2Shell. Our React2Shell vulnerability detection will simulate an attacker on your website. This is a benign attack which will not execute any code and only shows that RCE is possible. Rapid7 will validate the exploitability of the application and the associated risk.
How to run a React2Shell attack in the Rapid7 DAST
You can scan for this new RCE attack using either the new Arbitrary Code Execution attack template we have created or by creating your own custom attack template and selecting the RCE module. We have added some steps for you to follow below:
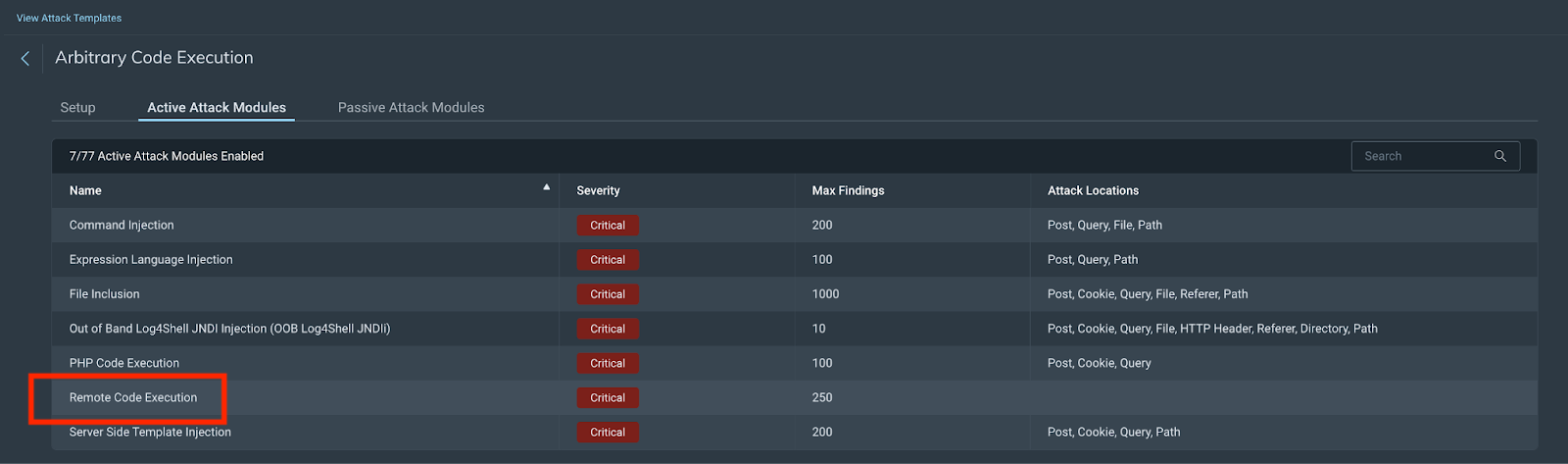
Default attack template option:
Choose the Arbitrary Code Execution attack template in your scan configuration:
⠀
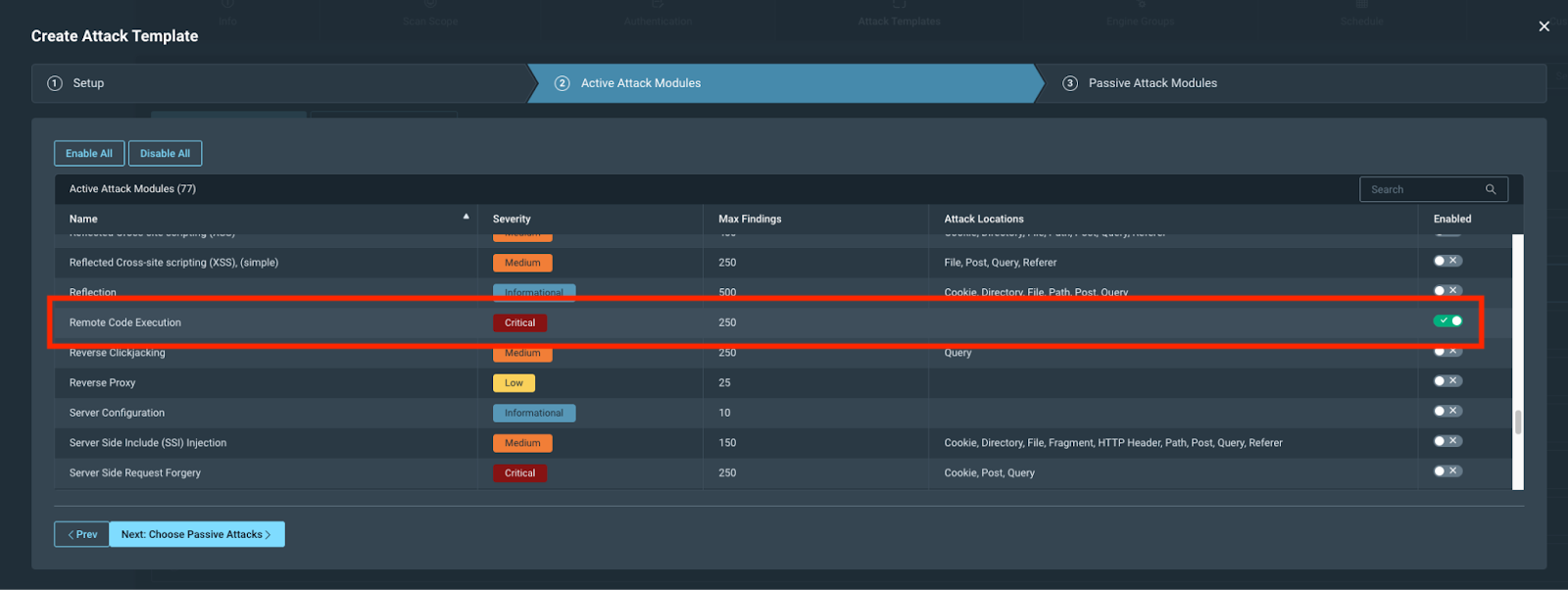
Custom attack template option:
Run a scan
Choosing the scan configuration you made earlier, scan against your selected app(s).
Scan results - React2Shell RCE finding
Now that you have run your scan, you can review the results to see if your app(s) have any findings. These will include remediation advice that you can follow.
⠀

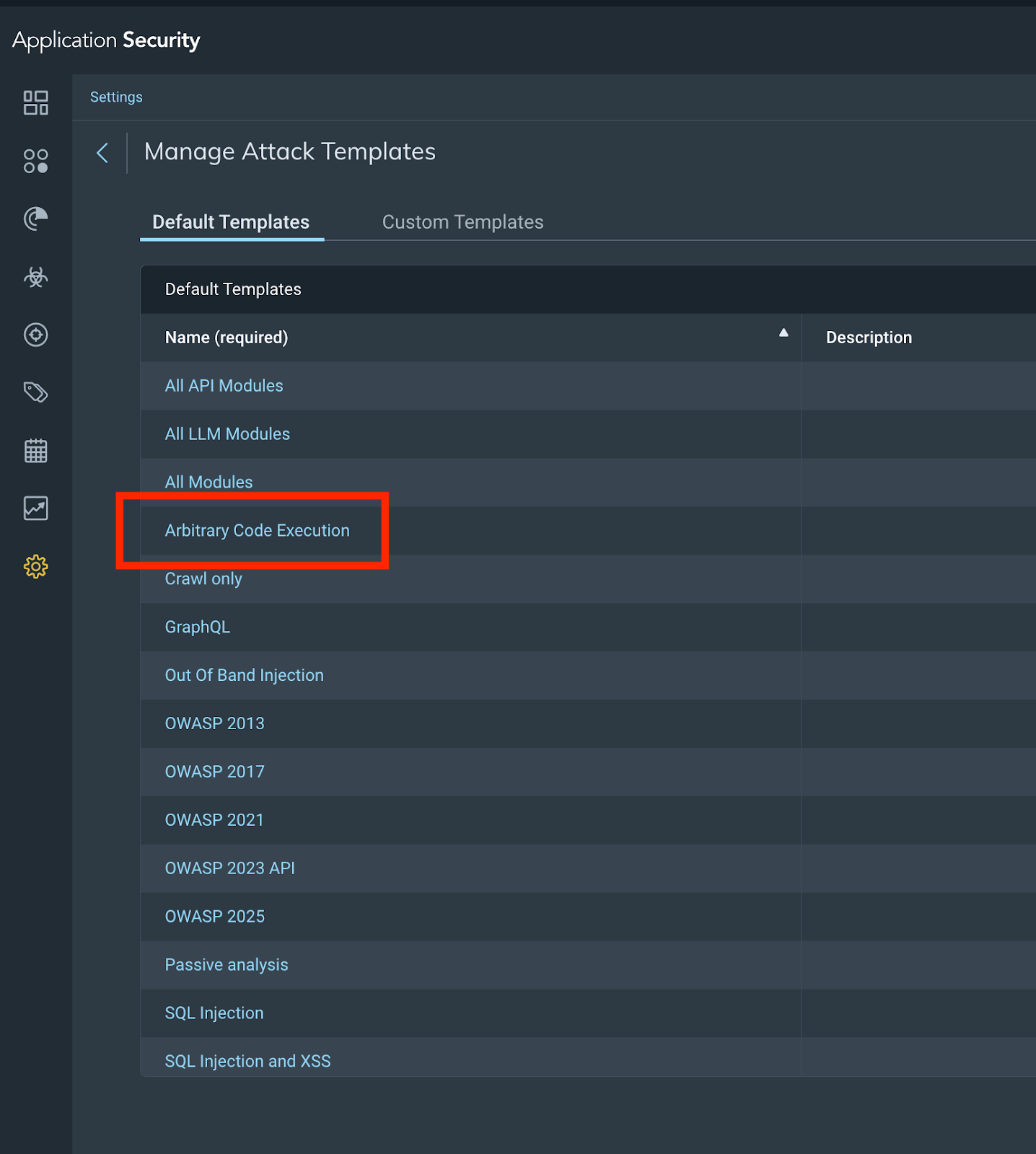
Manage attack templates
You can now manage your attack templates by navigating to the appropriate section and selecting the Arbitrary Code Execution attack template as below.
⠀
What’s next?
Patch immediately, upgrade React to 19.0.1, 19.1.2, or 19.2.1 (or newer). For Next.js, the recommended action is to update to the following respective patched versions: 15.2.6, 15.3.6, 15.4.8, 15.5.7, 16.0.7, or later*. You should seek to remediate this vulnerability on an urgent basis, outside of normal patch cycles and consider temporary web application firewall (WAF) rules for Flight endpoints while patching. If you’re looking to validate any fixes you have implemented, feel free to run a validation scan with our application security tool to verify the fixes are correct.
* For Next.js, the recommendation from Nextjs is to update to the following respective patched versions: 15.0.5, 15.1.9, 15.2.6, 15.3.6, 15.4.8, 15.5.7, 16.0.7, or later. However, we have identified that versions 15.0.5 and 15.1.9 have a different critical vulnerability and would recommend against using them.